3D Printing Services : 3D printing is a revolutionary technology that allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by printing layer upon layer of material. It has gained popularity in various industries, from automotive to healthcare, due to its ability to produce complex and customized designs with ease. There are several types of 3D printing methods, and one of them is metal 3D printing.
Metal 3D printing, also known as direct metal laser sintering (DMLS), involves the use of a laser to fuse metal particles together to create a solid object. This process allows for the production of intricate and detailed designs that may not be possible with traditional manufacturing methods.
The applications of metal 3D printing are vast and diverse. Here are some industries that can benefit from metal 3D printing services:
- Aerospace and Defense: Metal 3D printing can be used to create lightweight and complex parts for aircraft and military equipment, leading to improved performance and cost savings.
- Automotive: Metal 3D printing can be used to create customized and lightweight parts for cars, resulting in improved fuel efficiency and performance.
- Medical and Healthcare: Metal 3D printing has opened new possibilities in the medical field, allowing for the production of customized implants, prosthetics, and medical instruments.
- Industrial Manufacturing: Metal 3D printing offers flexibility in design, making it suitable for creating spare parts, prototypes, and small batches of products quickly and efficiently.
Utilizing metal 3D printing services has several benefits, including:
- Faster Production Time: Metal 3D printing can produce complex designs in a shorter time compared to traditional manufacturing methods, saving time and costs.
- Cost-Effective: Metal 3D printing eliminates the need for expensive tooling and allows for the production of complex designs in one piece, reducing production costs.
- Design Flexibility: Metal 3D printing allows for the production of intricate designs that may not be possible with traditional methods due to limitations in manufacturing processes.
When choosing a metal 3D printing service, consider factors such as the materials used, production capacity, quality and precision, and customer reviews and reputation. With the right partner, metal 3D printing can be a valuable tool for innovation and growth in various industries.
Key Takeaways:
- Metal 3D printing is a revolutionary technology that uses a variety of processes to create complex metal objects.
- Popular applications of metal 3D printing services include aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial manufacturing industries.
- When selecting a metal 3D printing service, consider factors such as materials used, production capacity, quality, and customer reviews.
What Is 3D Printing?
3D printing is a process used for manufacturing that constructs objects layer by layer from digital designs. It allows for the creation of intricate shapes using less material than traditional methods, making it a revolutionary technology for various industries.
Fun fact: In 2014, the first 3D printed car was produced, demonstrating the potential for large-scale 3D printing in the automotive sector.
What Are the Different Types of 3D Printing?
3D printing has revolutionized the world of manufacturing, allowing for the creation of intricate and complex designs with ease. But did you know that there are actually different types of 3D printing? In this section, we will explore the four main methods of 3D printing: fused deposition modeling, stereolithography, selective laser sintering, and digital light processing. Each technique has its own unique process and applications, making it important to understand the differences between them. So let’s dive into the world of 3D printing and discover the capabilities of each method.
1. Fused Deposition Modeling
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a 3D printing process that involves the following steps:
- Preparation of 3D model in CAD software.
- Slicing the model into layers using slicing software.
- Heating and extruding thermoplastic material layer by layer.
- Building the object from the bottom up.
For optimal results with FDM, it is important to use a suitable material, maintain correct print settings, and post-process for a refined finish.
2. Stereolithography
Stereolithography is a type of additive manufacturing process that utilizes a laser to solidify liquid resin layer by layer, resulting in the production of highly accurate and complex 3D printed components.
3. Selective Laser Sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is a 3D printing technique that utilizes a high-powered laser to fuse small particles of plastic, metal, ceramic, or glass powders into a solid mass with the desired 3D shape.
The process of selective laser sintering involves several steps:
- First, the preparation of a CAD model of the object to be printed.
- Next, the CAD model is converted into thin cross-sectional layers using specialized software.
- Then, the powdered material is fused layer-by-layer using a laser, based on the cross-sectional information.
- This layering and fusing process is repeated until the entire object is successfully created.
Fun fact: Selective laser sintering is widely used in the production of functional prototypes, end-use parts, and manufacturing tooling for various industries.
4. Digital Light Processing
Digital Light Processing (DLP) is a 3D printing technique that utilizes light to solidify layers of resin in order to produce objects. With its high-resolution printing and fast production speeds, DLP is ideal for creating intricate and detailed parts for a variety of applications.
In the 1980s, Charles Hull developed the first 3D printing technology, Stereolithography (SLA), which laid the groundwork for future advancements in additive manufacturing.
What Is Metal 3D Printing?
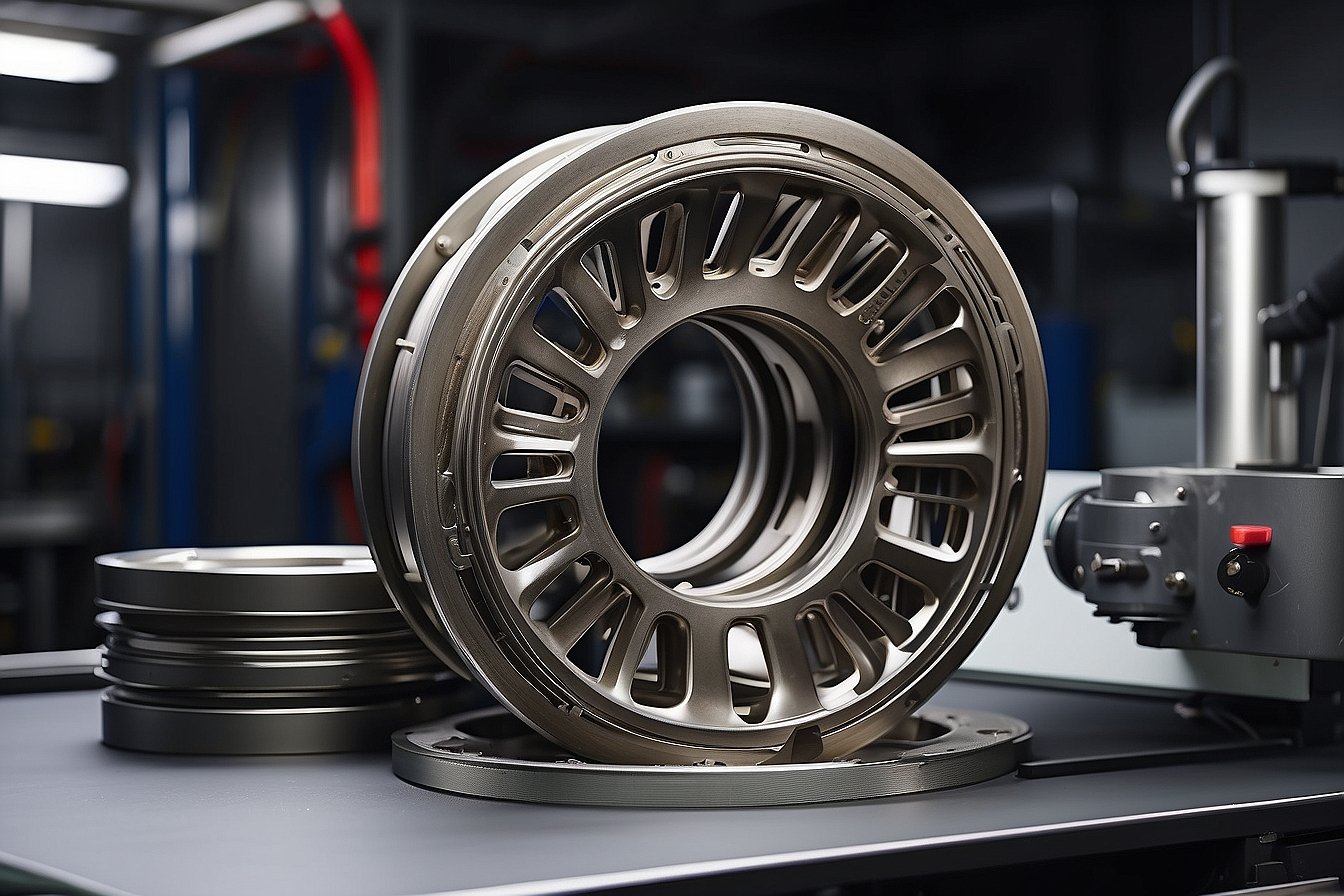

Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is the process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering metal powder and fusing it together with a laser. This cutting-edge method enables the production of intricate designs and complex metal parts that may be challenging or even impossible to make using traditional techniques.
Important factors to consider when exploring metal 3D printing include choosing the right materials, designing the part effectively, and utilizing appropriate post-processing techniques. Before embarking on a metal 3D printing project, it is essential to research reputable service providers and fully understand the specific requirements of your project.
How Does Metal 3D Printing Work?
- Preparation: The process of metal 3D printing begins with creating a 3D model using computer-aided design (CAD) software.
- Slicing: Next, the 3D model is sliced into thin horizontal layers.
- Printing: The metal 3D printer then follows the instructions from the sliced model, layering metal powder and using a laser or electron beam to fuse the particles together.
- Post-processing: After the printing is complete, any excess powder is removed, and the part undergoes heat treatment and other finishing processes to enhance its properties.
What Are the Applications of Metal 3D Printing?
The emergence of metal 3D printing has revolutionized various industries, offering new possibilities and capabilities for manufacturing. In this section, we will explore the wide range of applications for metal 3D printing and how it is being utilized in different sectors. From aerospace and defense to automotive and healthcare, we will delve into the specific uses of metal 3D printing and its impact on industrial manufacturing. Join us as we uncover the diverse applications of this cutting-edge technology.
1. Aerospace and Defense
- Specialized Components: Metal 3D printing in the aerospace and defense industries involves creating intricate and lightweight components, such as turbine blades and brackets.
- Prototyping: Companies use metal 3D printing to quickly produce prototypes of parts for testing and validation in the aerospace and defense sectors.
- Customization: Metal 3D printing allows for the customization of parts to meet specific requirements in aerospace and defense applications.
- Reduced Weight: By utilizing metal 3D printing, the aerospace and defense industries can design components with complex geometries, reducing overall weight without compromising strength.
2. Automotive
- The incorporation of 3D printing technology in the automotive industry allows for rapid prototyping, customized parts production, and lightweight component manufacturing.
- With enhanced design freedom, intricate and complex geometries can be achieved, optimizing part performance and vehicle efficiency.
- When it comes to material selection, it is crucial to consider metal 3D printing as it offers durable and high-strength components suitable for automotive applications.
When searching for metal 3D printing services for automotive needs, it is important to prioritize expertise in automotive-grade materials and a proven track record of precision and reliability.
3. Medical and Healthcare
- Medical Devices: Metal 3D printing is utilized for the creation of personalized implants, prosthetics, and surgical tools.
- Biomedical Research: It assists in the development of prototypes for medical equipment and components used for research purposes.
- Tissue Engineering: Metal 3D printing plays a crucial role in producing scaffolds for tissue regeneration.
When considering metal 3D printing services for medical and healthcare applications, it is important to prioritize materials that are suitable for medical use, offer high precision, and have positive customer feedback to ensure optimal outcomes.
4. Industrial Manufacturing
Industrial manufacturing is just one of the many applications of metal 3D printing, with its use spanning across sectors such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare. This technology allows for the production of complex parts, rapid prototyping, and customization. Utilizing metal 3D printing services comes with numerous advantages, including reduced production time, cost-effectiveness, and design flexibility.
When choosing a metal 3D printing service, it is important to consider factors such as:
- The materials used
- Production capacity
- Quality standards
- Customer reviews and reputation
What Are the Benefits of Using Metal 3D Printing Services?
When it comes to 3D printing, metal is a highly sought-after material due to its durability and versatility. But what sets metal 3D printing services apart from other methods? In this section, we will discuss the benefits of using metal 3D printing services. From faster production times to cost-effectiveness and design flexibility, we will explore how this technology can revolutionize the way we create and manufacture metal products. So let’s dive into the advantages that metal 3D printing has to offer.
1. Faster Production Time
- Choose state-of-the-art metal 3D printers with high-speed capabilities.
- Incorporate efficient production processes such as Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
- Utilize automated post-processing technologies to expedite finishing.
Fact: Metal 3D printing has the potential to reduce production times by up to 90% compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
2. Cost-Effective
- Consider the cost-effectiveness of each part and the overall production cost.
- Assess the impact of design modifications on cost and expenses.
- Evaluate the expenses associated with post-production processes.
The concept of cost-effectiveness in metal 3D printing dates back to the early 2000s when advancements in technology and materials made it more feasible for industrial applications.
3. Design Flexibility
- Consider the capability to produce complex geometries and intricate designs.
- Evaluate the freedom to create customized, lightweight, and optimized parts.
- Assess the potential for rapid prototyping and iterative design improvements.
Did you know? Metal 3D printing allows for design flexibility with the ability to create intricate and highly detailed designs, offering unparalleled design freedom.
What Are the Factors to Consider When Choosing a Metal 3D Printing Service?
As the demand for metal 3D printing continues to rise, so does the number of service providers offering this cutting-edge technology. However, not all 3D printing services are created equal, especially when it comes to metal printing. In this section, we will discuss the key factors to consider when choosing a metal 3D printing service. From the materials used to the production capacity and the overall quality and precision of the final product, we will guide you through the important considerations to help you make an informed decision. Additionally, we will also touch upon the role of customer reviews and reputation in this process.
1. Materials Used
- Aluminum: Suitable for aerospace and automotive parts due to its lightweight and durable nature.
- Stainless Steel: Ideal for functional prototypes, tooling, and end-use parts in various industries.
- Titanium: Commonly used in medical and aerospace applications due to its biocompatibility and high strength-to-weight ratio.
- Nickel Alloys: Utilized in high-temperature applications such as gas turbine components and chemical processing equipment.
When considering the materials used for 3D printing, it is important to take into account the specific requirements of your project. Consulting with experts in the field can provide valuable insights in choosing the appropriate metal for your project.
2. Production Capacity
- Evaluate the service provider’s production capacity, making sure it meets the requirements of your project.
- Assess their capability to handle large or complex projects within the given timelines.
- Consider the variety of materials that the service is capable of handling for diverse production needs.
When choosing a metal 3D printing service, prioritize those with a proven track record in managing projects of similar size and complexity
3. Quality and Precision
- Utilize advanced metal 3D printing techniques like Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) or Electron Beam Melting (EBM) to ensure high levels of precision.
- Partner with established and trustworthy metal 3D printing service providers to guarantee tight tolerances and accuracy.
- Confirm adherence to quality standards by obtaining certifications such as ISO 9001 for quality management systems.
When selecting metal 3D printing services, prioritize precision and quality to achieve optimal results for your projects.
4. Customer Reviews and Reputation
- Customer Reviews: When choosing services, prioritize those with positive customer feedback, as it indicates reliability and satisfaction.
- Reputation: Opt for providers with a strong reputation for consistently delivering high-quality metal 3D printing services.
Also Refer : Boost Your Website’s Security With Cloud Web Security Services
Frequently Asked Questions
What is metal 3D printing and how does it work?
Metal 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating 3-dimensional objects by adding thin horizontal layers of metal powder and binding agents together using advanced technology, such as high precision lasers. The process involves designing a 3D model on a computer, slicing it into thin layers, and then using a metal 3D printer to fuse these layers together to create the desired object.
What are the benefits of using metal 3D printing services?
There are several benefits to using metal 3D printing services, such as the ability to create complex and intricate designs, reduced lead times, and the production of fully dense parts. Metal 3D printed parts also have high aesthetic value, good mechanical properties, and are suitable for high load applications due to their strength and low weight.
What materials can be used in metal 3D printing?
Some of the materials that can be used in metal 3D printing include aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, maraging steel, copper, and cobalt chrome. Each material has its own unique properties and cost, with aluminum being the most affordable and titanium being the most expensive.
What is the difference between DMLS and metal binder jetting?
DMLS (direct metal laser sintering) and metal binder jetting are two different types of metal 3D printing processes. DMLS involves sintering layers of metal powder with a laser, while metal binder jetting uses a binding agent to fuse metal powder particles together. DMLS is typically used for end-use parts and production, while metal binder jetting is ideal for creating prototypes and appearance models.
How do metal 3D printing services ensure quality production?
Metal 3D printing services, such as Quickparts, have knowledgeable experts guiding the production process and qualified operators with experience in metal 3D printing. They also use advanced equipment and techniques, such as high-precision lasers and multi-step processes, to ensure the production of fully dense and high-quality parts.
What are the surface finish options for metal 3D printed parts?
Metal 3D printing services offer a variety of surface finishes for their parts, including brushed surfaces, polished mirror finishes, sandblasting, bead blasting, anodizing, painting, and powder coating. These finishes can improve the appearance, durability, and functionality of the parts and can be customized to the client’s needs.